Local Government Financial Stress and Drinking Water Resilience
This research is funded by the National Science Foundation in collaboration with Christine Kirchhoff at Penn State University.
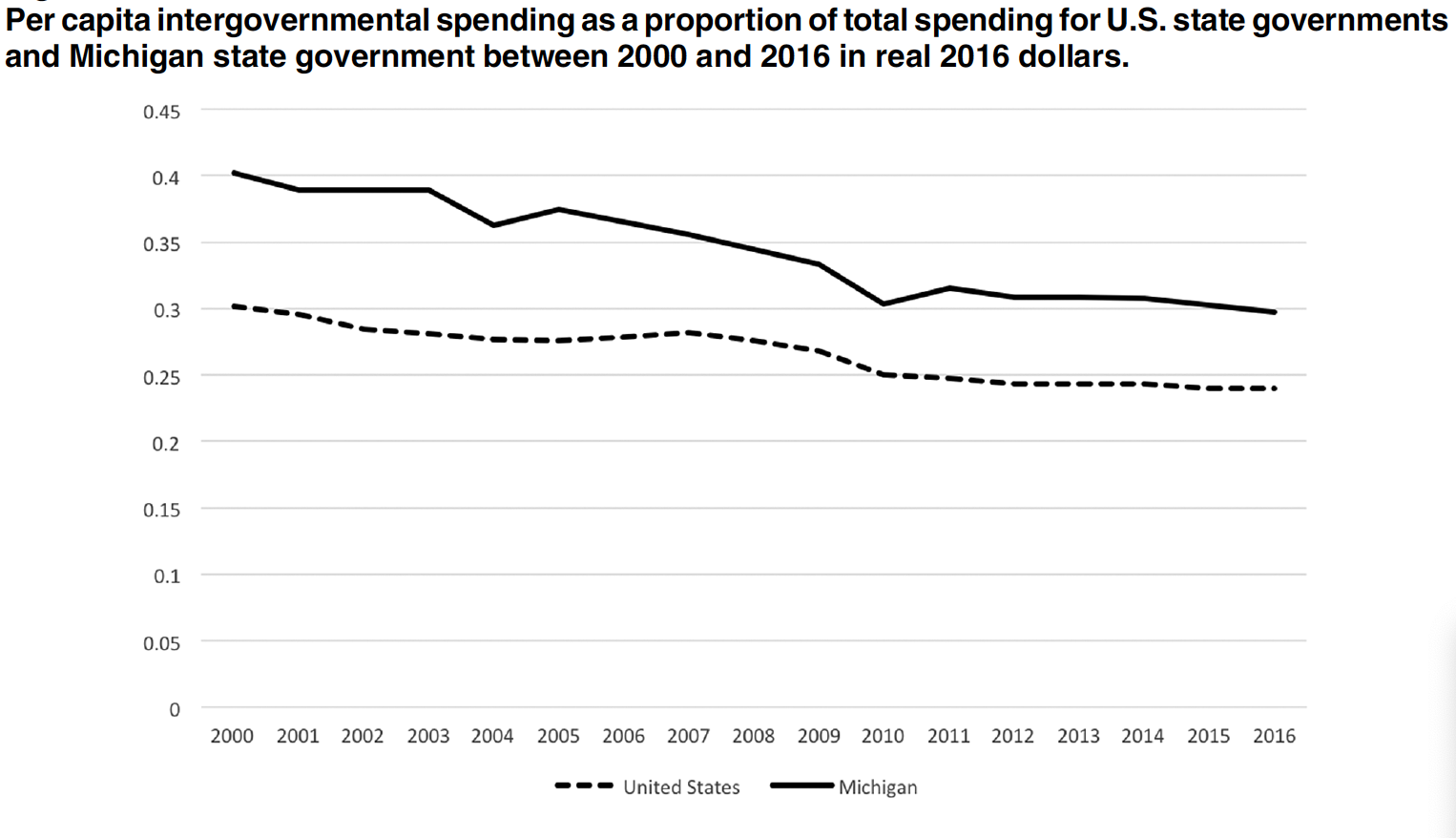
Decision-making under financial stress is a pervasive challenge in U.S. city governments, with unknown implications for the resilience of public services upon which millions of people depend.
Across the nation, cities face immense fiscal stress brought about by the confluence of increased demands for critical city services – including drinking water, education, transportation, fire protection, and housing – and precipitous declines in revenues needed to support those increased demands. Decisions made under conditions of fiscal stress may erode and undermine the resilience of these critical city services by impeding the ability of water managers to respond to today’s challenges and plan for an uncertain future, while maintaining affordable and equitable service delivery.
Despite these risks, the effects of financial stress on decision-making by city governments and the influence of local political, institutional, and physical contexts on decision-making is poorly understood. This NSF-funded research will advance understanding of the ways that financial stress affects decision-making and resilience of drinking water systems (DWS), produce actionable knowledge that will improve equity and resilience of DWS, generate a new, publicly accessible database, and educate and train students and water professionals about the intersection of fiscal stress, risk and resilience, and equity in municipal decision making.
A key contribution of this project is the City Water and Finance Database, a new public resource that identifies municipal drinking water systems throughout the U.S. Stay tuned for the public release in 2023!